Bone Grafts
Bone grafting is the most common surgical dental procedure associated with dental implants. It is vital that dentists placing dental implants be proficient at bone grafting techniques or knowledgeable enough to diagnose them and refer the patient to an oral surgeon to have that particular procedure done.
The most important requirement for a successful dental implant and bone grafting procedures is the presence of enough bone height and width to support the implant. There are several types of dental bone grafting procedures related to dental implants:
Socket preservation
Socket preservation is where the bone is placed in the tooth socket after extraction to preserve the height and width usually for future dental implant.
Ridge augmentation
Ridge augmentation refers to the process of rebuilding the height or width of the jaw bone or both to allow for a future dental implant. This procedure is usually performed in areas with considerable bone loss. Ridge augmentation can be accomplished utilizing various surgical methods and techniques. These surgical techniques vary in their use depending on your dentist’s training and experience, your condition and whether it is an upper or lower jaw. The details of this particular procedure can further be discussed during your consult, since the surgical approach varies from patient to patient.
Dental Ridge Augmentation Before Image
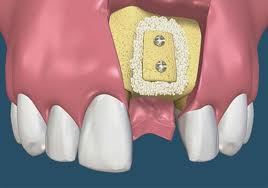
Dental Ridge Augmentation After Image
Periodontal “Tissue” Grafts
Periodontal gum tissue grafts are an important part of implant dentistry. There is two types gum tissue around teeth. Thick gum tissue immediately surrounds teeth and is referred to as (keratinized gum tissue) or (non-mobile gum tissue) or (keratinized gingiva) and thin tissue that lies close to the floor of the mouth that is referred to as (non-keratinized gum tissue) or (mobile gum tissue) or (non-keratinized gingiva).
This thick tissue is vital to the health and longevity of teeth. Loss of the thick keratinized tissue is referred to as gum recession or gingival recession. When that happens, the lost tissue must be replaced. Loss of keratinized tissue is common with dental implants as it is a common consequence of tooth loss.
There several methods and materials utilized in tissue or gum grafting:
1. Connective tissue grafts:
The graft is taken from the deeper tissue of the roof of the mouth and grafted to the deficient site.
2. Free gingival grafts:
The grafted tissue is taken from the outer surface of the roof of the mouth and grafted to the deficient site.
3. AlloDerm tissue graft:
AlloDerm is donated skin Allograft material from other humans that is processed to produce a dermis layer “the deeper layer of the skin”. The main advantage of AlloDerm grafts is less healing as there is no donor site at the roof of the mouth. Recently other allograft material within this category have been developed.
4. Periodontal tunnel grafts or periodontal tunneling surgery:
Grafting gum tissue with tunneling techniques is a part of the latest development in periodontal “gum” microsurgery techniques also referred to as periodontal plastic microsurgery. It is well understood that less invasive surgery would lead to less disruption to blood supply and in turn faster wound healing and more predictable results. Several variations of this method have been developed, these methods are referred to as “modified periodontal tunneling surgery” or “modified periodontal tunnel grafts”. This is the most utilized type of periodontal tissue grafting surgery at Dental Dynamics as it produces the most predictable results.
Before Periodontal “Gum” Graft
After Periodontal “Gum” Graft
Periodontal Tissue Graft By Dr. Saleh Using the Tunneling Technique
5. Growth Factors “PDGF” and Periodontal Tissue Grafts:
In certain cases growth factors can be used along with gum grafting. The most utilized is PDGF “platelet derived growth factors”. PDGF can promote the regeneration of periodontal “tissue” and healing. There are several techniques utilized in incorporating PDGF growth factors into periodontal tissue grafts .
6. Placental tissue for periodontal tissue grafts:
The most recent innovation in periodontal and gum tissue is the utilization of placental tissue. It is thought to produce less inflammation than other donated allograft materials currently used.
Before Sinus Lift
Sinus Lift and Dental Implant Placement
Sinus Lift
Sinus Lift is the process where the sinus membrane is repositioned to allow for a space where bone is grafted to support a dental implant. Sinus lift is a very predictable procedure that can increase bone height and width. In most cases the dental implant(s) is placed along with the sinus lift procedure.
There are several direct and indirect techniques that can be used for sinus lift procedures. Further details of the sinus lift technique that is most suitable for your situation will be discussed during your consult.
Types of Bone Materials Used In Dental Bone Grafting:
1. Autografts:
The bone comes from the same “patient” person, while the recipient site is the jaw, the donor site can be part of mandible or hip.
2. Allografts:
Bone that comes from other humans, usually processed cadaver bone in the form of small granules or small blocks.
3. Xenografts:
Bone from another species, most commonly from cows
4. Alloplasts:
Synthetic bone material. Material that is manufactured.
Growth factors and Dental Bone Grafting:
These growth factors can be mixed with the dental bone grafts and can expedite the bone formation and healing.
1. Platelet Rich Plasma or PRP
Platelet Rich Plasma or is a growth factor that comes from the patient, also called autogenously growth factor. A process where a blood sample taken from the patient prior to the bone grafting procedure and placed in a centrifuge for few minutes to separate the plasma from the rest of the blood. The net product is PRP. PRP can be mixed with the bone graft, or placed on top of it or both. Depending on the process of centrifuging, time and speed, different forms of PRP may be produced such as PRF “plasma rich fibrin. PRP and other forms of PRP can expedite wound healing and recovery. It is particularly beneficial in patients with compromised immunity as in diabetes.
“Dr Saleh believes that PRP is a great adjunct to implant surgery particularly in elderly patients and patients with compromised immunity”
PRP is offered at Dental Dynamics, located in Portland, Oregon (Pearl District).
2. Platelet Derived Growth Factors or PDGF:
PDGF is a synthetic growth factor. There are several growth factors subtypes within this category. hPDGF-BB is most commonly used under product name GEM21S. This is a bone like synthetic matrix that is enhanced with growth factor. While PRP comes from the patients, PDGF-BB is produced by tissue engineering methods, PDGF products tend to be used mostly with soft tissue “gum” grafting procedures.
3. Bone morphogenetic protein or BMP:
BMP is most recent development in growth factor technology. The most commonly used is recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein or rhBMP-2 under product name INFUSE. It serves as one of the latest alternatives to grafting patients own bone. It is the most powerful growth factor on the market today.
These growth factors vary in their ability to enhance wound healing, bone regeneration and differ in their applications. PRP is the least potent while rhBMP-2 is the most potent and most effective in wound healing and regeneration of bone. During your consult, we can discuss the most suitable bone grafting material and method for your particular situation.
Sinus Elevation and Sinus Lift Techniques
Sinus lift or sinus elevation or sinus augmentation is where sinus membrane is repositioned to create a space that is filled with bone graft to support a dental implant. Sinus lift is a very predictable procedure that can increase bone height and width to accommodate adequate implant placement. In most cases the dental implant can be placed along with the sinus lift procedure.
There are several methods by which this procedure can be performed depending on how the sinus membrane is repositioned:
1. Direct Sinus Lift or Lateral Window Sinus Lift:
A small opening on the side of the upper jaw is utilized to access and lift the sinus membrane. This is the most utilized way of sinus lift or sinus elevation as it provides the most visualization and predictability.
Direct Sinus Lift
2- Indirect Sinus Lift Osteotome Sinus Lift
In these methods of sinus elevation, access is from the top of the bone ridge without visualizations of the membrane. A small opening is created at the top of the ridge leaving 1-2mm bone coverage of the sinus. The 1-2mm remaining boney shell is then pushed gently and separated against sinus with an osteotome “dental sinus elevation instrument”. The sinus is then elevated via one of several methods:
Sinus elevation specialized Instruments:
Specialized instruments are used to reposition the sinus membrane.
Balloon Technique:
An air filled balloon is used to apply pressure against the sinus membrane to reposition it.
Hydraulic “water” Pressure:
Water pressure is used to reposition the sinus membrane.
Sinus Lift Indirect Technique Using Water Pressure
The main disadvantage of this method is lack of visualization of the sinus membrane as the implant dentist must rely on accurate measurements and tactile feel. The biggest advantage is faster healing as this procedure is less invasive than the traditional lateral window method of sinus elevation. Both direct sinus lift and indirect sinus lift techniques are utilized at Dental Dynamics, Portland, Oregon (Pearl District).
Flapless “No Incision” Dental Implant Surgery
Flapless dental implant surgery is the type of implant surgery where incisions are not utilized during the surgery. The use of CT scans and computer guided implant placement techniques has allowed us to be able to place dental implants directly through the gums without the need to visualize the bone. This is because the CT scan gives an accurate three dimensional representation of the bone and surrounding structures. Flapless dental implant surgery allows for faster healing, less inflammation and less post-op discomfort and pain. In some cases flapless surgery may not be possible and traditional techniques may be indicated. During your complimentary implant consult, Dr Saleh will discuss if this type of implant surgery is possible in your situation.
Flapless Dental Implant Surgery by Dr Saleh
Flapless Implant Surgery Before
Flapless Implant Surgery Immediately After